Distributed traffic signal control for large-scale traffic networks
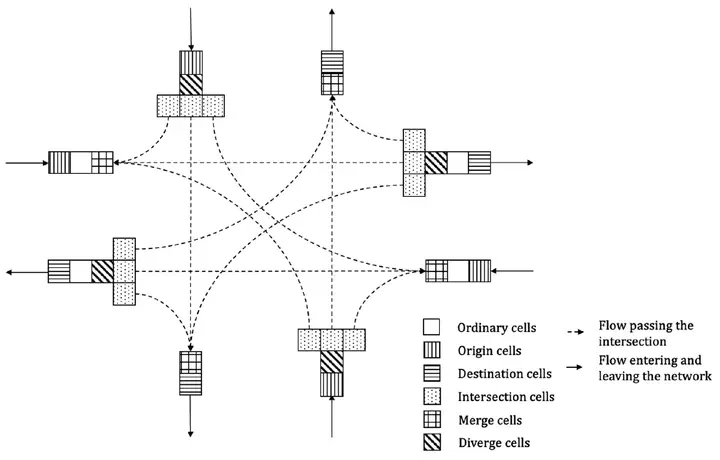 CTM signalized intersection
CTM signalized intersectionRelated Publications
Overview
The diverse and complex real-world network topology presents a significant challenge for network-level traffic control. My collaborators and I explored two distinct approaches: 1) an optimization-based method and 2) a max-pressure-based control method.
In the optimization-based approach, we combined the ADMM (alternating direction method of multipliers) with Bender’s decomposition to tackle network-level traffic control under uncertainty. Despite utilizing advanced optimization and parallel computing techniques, the problem remained challenging to solve. This highlights the promise of the max-pressure control method – a distributed control algorithm that is provably throughput-optimal. However, the original max-pressure control algorithm does not account for phase switching losses caused by intersection clearance time and only guarantees bounded queue lengths rather than minimizing them. To address these limitations, I introduced a hysteresis phase switching mechanism and integrated reinforcement learning (RL) with max-pressure control to further enhance the controller’s performance. As a distributed controller that relies solely on neighbor observations, this proposed approach holds significant potential for real-world implementation.